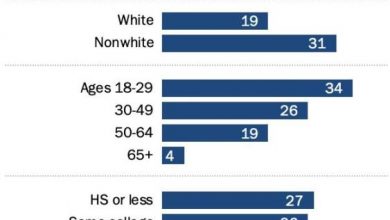
Best Practices for Web Accessibility Compliance
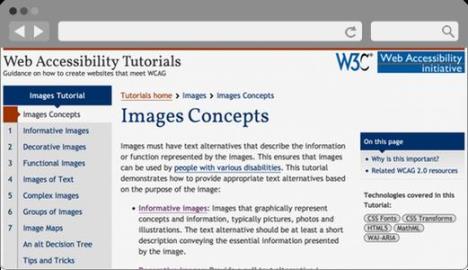
Best Practices for Web Accessibility Compliance
Introduction
Web accessibility compliance has become a crucial factor in website development. Ensuring that your website is accessible to people with disabilities not only meets legal requirements but also creates an inclusive online environment for all users. In this blog post, we will discuss some best practices to achieve web accessibility compliance.
Understanding Web Accessibility
What is web accessibility?
Web accessibility refers to designing and developing websites that can be accessed and used by people with disabilities. This includes making your website perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for everyone, regardless of their abilities.
Why is web accessibility important?
Web accessibility is important for various reasons. Firstly, it ensures equal access to information and services for people with disabilities. Secondly, it improves user experience for all users, including those without disabilities. Moreover, web accessibility compliance is mandated by laws like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), which protects the rights of disabled individuals.
Best Practices for Web Accessibility Compliance
Use Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML helps screen readers and assistive technologies understand the structure and content of your website. Use the appropriate HTML tags to create well-organized and meaningful content. For example, use proper heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to indicate the hierarchy of information on your page.
Provide Alternative Text (Alt Text) for Images
Add descriptive alt text to all images on your website. Alt text provides a textual alternative to images for those who cannot see them. Be concise and descriptive in your alt text, conveying the purpose and content of the image.
Ensure Keyboard Accessibility
Not all users can operate a mouse, so it’s important to make sure your website is fully navigable using only a keyboard. Enable keyboard shortcuts, support the Tab key for sequential navigation, and ensure that the focus indicator is visible to allow users to understand their location on the page.
Provide Captions and Transcripts for Multimedia
If your website includes multimedia content like videos or audio files, make sure to provide captions or transcripts. Captions enable deaf or hard-of-hearing users to understand the audio content, while transcripts allow users to access the information without the need for audio.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are there any guidelines or standards for web accessibility compliance?
Yes, there are several guidelines and standards for web accessibility compliance. The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1, developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), provide detailed guidance on making websites accessible to all users.
Q: What are some common disabilities that web accessibility aims to address?
Web accessibility aims to address various disabilities, including visual impairments, hearing impairments, cognitive disabilities, motor disabilities, and more. Designing your website with these disabilities in mind ensures a wider reach and better user experience for all users.
Q: How can I test the accessibility of my website?
There are several tools and methods available to test the accessibility of your website. Automated tools like Wave and Axe can scan your website for common accessibility issues. Additionally, conducting manual testing with screen readers and assistive technologies can provide valuable insights on the user experience for disabled individuals.
Conclusion
Adhering to web accessibility compliance not only makes your website inclusive for people with disabilities but also improves the overall user experience for all users. By following the best practices mentioned in this blog post, you can ensure that your website is accessible and meets the required standards. Remember, accessibility should be a fundamental part of your website development process from the start.